In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital technology, edge computing and cloud computing stand out as transformative forces. Each offers distinct benefits, but together, they create a synergistic approach that enhances performance, reduces latency, and brings a myriad of advantages to businesses and consumers alike. This blog explores how edge computing integrates with cloud services, the benefits of this integration, and real-world use cases illustrating its impact.
Understanding Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
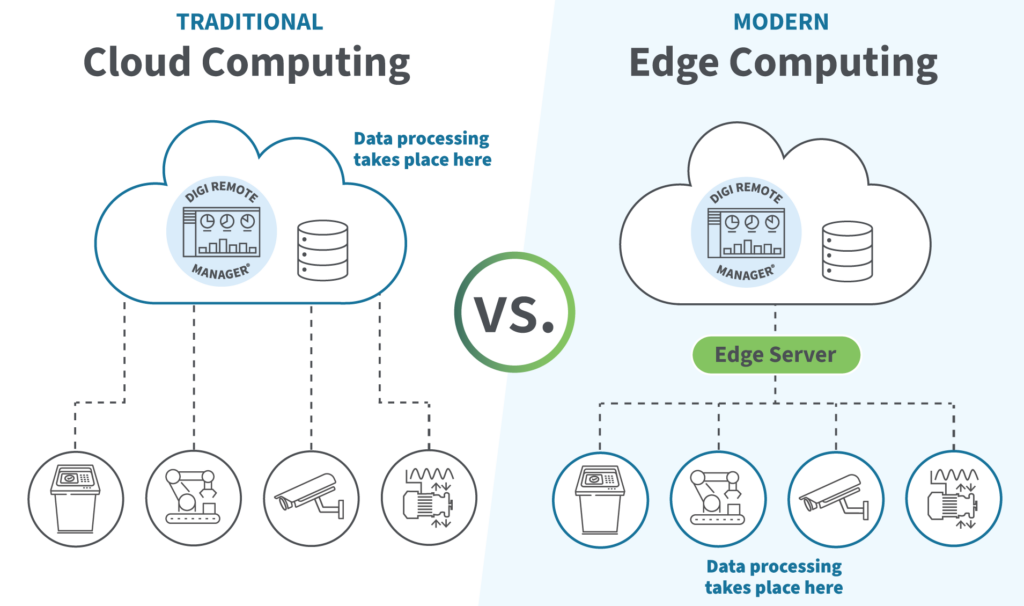
Edge Computing refers to the practice of processing data closer to the source of data generation rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. By bringing computation and storage closer to the devices generating the data, edge computing reduces the distance data must travel, thereby decreasing latency and bandwidth usage.
Cloud Computing, on the other hand, involves delivering computing services—such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics—over the internet (“the cloud”). Cloud computing enables scalable, on-demand access to resources and services, providing flexibility and cost-efficiency.
The Integration of Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
The integration of edge computing with cloud services leverages the strengths of both paradigms. Edge computing provides real-time data processing at the source, while cloud computing offers extensive storage, advanced analytics, and powerful computing capabilities. This hybrid approach results in several key benefits:
- Reduced Latency: By processing data at the edge, near the data source, the integration minimizes the time it takes for data to travel to and from the cloud. This is crucial for applications requiring real-time responses, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and augmented reality.
- Bandwidth Optimization: Edge computing reduces the amount of data that needs to be sent to the cloud for processing. This optimizes bandwidth usage and reduces costs associated with data transfer, particularly important in environments with limited bandwidth.
- Improved Reliability: Edge computing can continue to function independently of the cloud, providing resilience and reliability. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios where constant cloud connectivity cannot be guaranteed, such as remote locations or during network outages.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy: By processing sensitive data locally at the edge, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches during transmission. This is especially relevant for applications dealing with personal data, such as healthcare or finance.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The integration allows businesses to scale their operations efficiently. Cloud services can handle large-scale data storage and complex computations, while edge devices manage real-time processing and localized tasks.
Real-World Use Cases of Edge and Cloud Integration
- Smart Cities:
Smart cities use edge computing to manage real-time data from various sensors and devices, such as traffic lights, surveillance cameras, and environmental sensors. By processing data locally, cities can respond instantly to changing conditions, improving traffic flow, enhancing public safety, and managing resources more efficiently. The cloud provides the overarching infrastructure for data aggregation, advanced analytics, and long-term storage, allowing city planners to make informed decisions based on comprehensive insights. - Healthcare:
In healthcare, edge computing enables real-time patient monitoring through wearable devices and smart medical equipment. For example, continuous glucose monitors and heart rate monitors can process data locally to provide immediate alerts and insights. This local processing is critical for timely interventions in critical care situations. Meanwhile, cloud computing stores patient data, supports advanced analytics, and facilitates telemedicine services, providing healthcare professionals with a holistic view of patient health and enabling remote consultations. - Industrial IoT:
Manufacturing and industrial sectors leverage edge computing to enhance operational efficiency and predictive maintenance. Edge devices installed on machinery can monitor performance, detect anomalies, and predict maintenance needs in real-time. This prevents costly downtime and extends the lifespan of equipment. Cloud computing aggregates data from multiple sources, providing comprehensive analytics, machine learning capabilities, and strategic insights to optimize overall production processes and supply chain management. - Autonomous Vehicles:
Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on low-latency data processing to make real-time driving decisions. Edge computing plays a crucial role in processing data from sensors and cameras within the vehicle to detect obstacles, pedestrians, and other vehicles instantaneously. The cloud supports long-term data storage, route optimization, and fleet management. By integrating edge and cloud computing, autonomous vehicles can operate safely and efficiently while leveraging cloud-based insights for continuous improvement. - Retail:
In the retail sector, edge computing enables real-time inventory management, personalized customer experiences, and efficient checkout processes. Smart shelves and point-of-sale systems process data locally to manage stock levels and provide instant recommendations to customers. Cloud computing supports large-scale data analysis, customer relationship management (CRM), and targeted marketing campaigns, enhancing overall business strategy and customer engagement.
The Future of Edge and Cloud Integration
As technology continues to advance, the integration of edge computing and cloud services is expected to become even more seamless and sophisticated. Emerging technologies like 5G will play a significant role in enhancing the capabilities of edge computing, providing faster and more reliable connectivity. This will further reduce latency and enable more complex and data-intensive applications to benefit from edge processing.
Moreover, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will enhance the analytical capabilities at the edge. Edge devices will increasingly incorporate AI/ML models to process data in real-time, making more intelligent decisions locally. The cloud will continue to serve as the central hub for training and updating these models, ensuring that edge devices benefit from the latest advancements in AI/ML technologies.
Conclusion
The integration of edge computing with cloud services represents a powerful paradigm shift in how data is processed, stored, and analyzed. By combining the strengths of both approaches, organizations can achieve reduced latency, optimized bandwidth, improved reliability, enhanced security, and greater scalability. This hybrid approach is transforming industries, driving innovation, and creating new opportunities for businesses to thrive in the digital age.As we look to the future, the synergy between edge and cloud computing will only grow stronger, enabling more sophisticated applications and delivering unprecedented value. Businesses that embrace this integration will be well-positioned to navigate the complexities of the modern digital landscape, unlocking new levels of performance, efficiency, and competitive advantage
